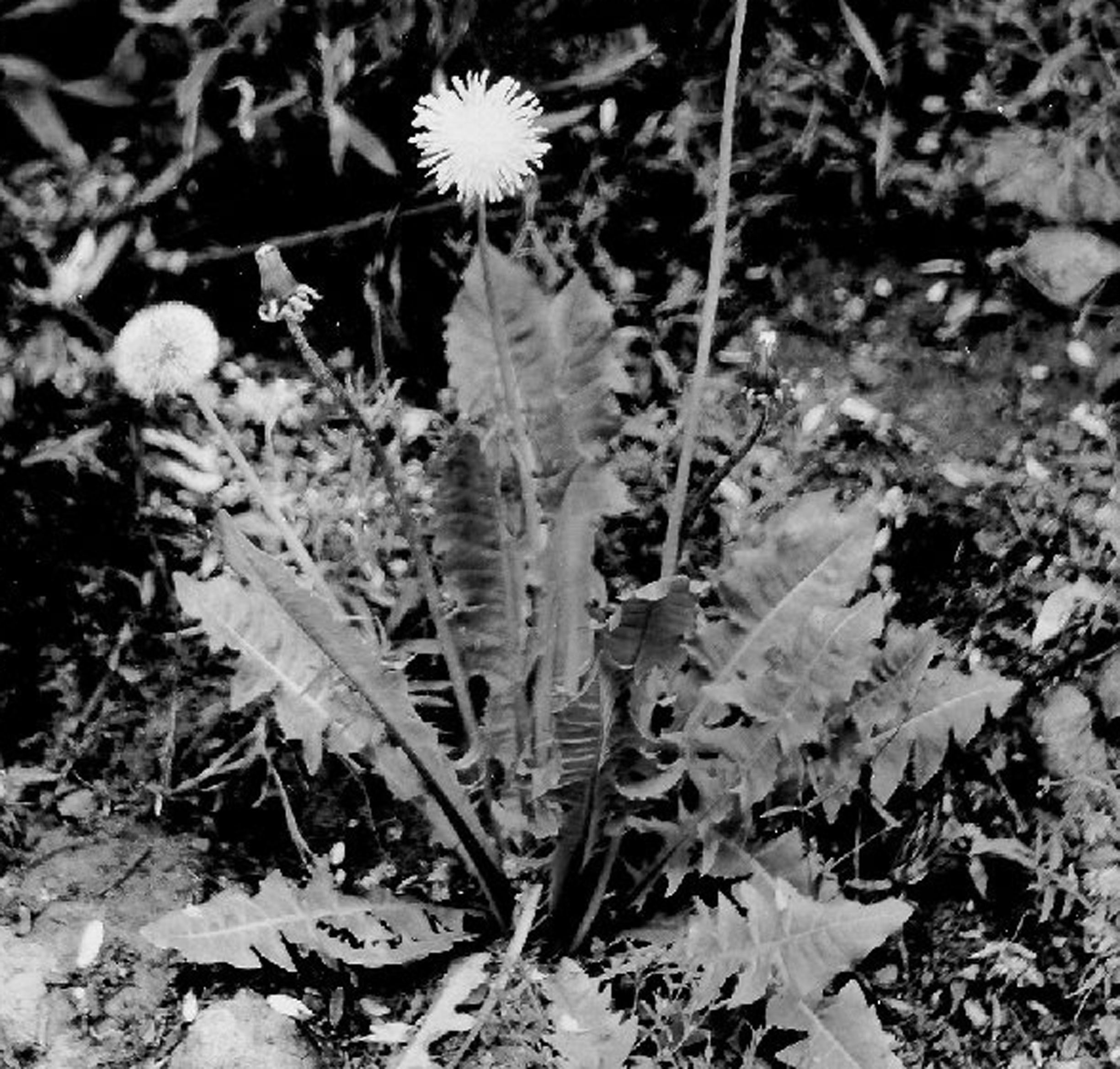
Dandelion
(Taraxacum F.H. Wigg.)

USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / Britton, N.L., and A. Brown. 1913.
An Illustrated Flora of the Northern United States, Canada and the British Possessions. 3 vols. Charles Scribner's Sons, New York. Vol. 3: 316.
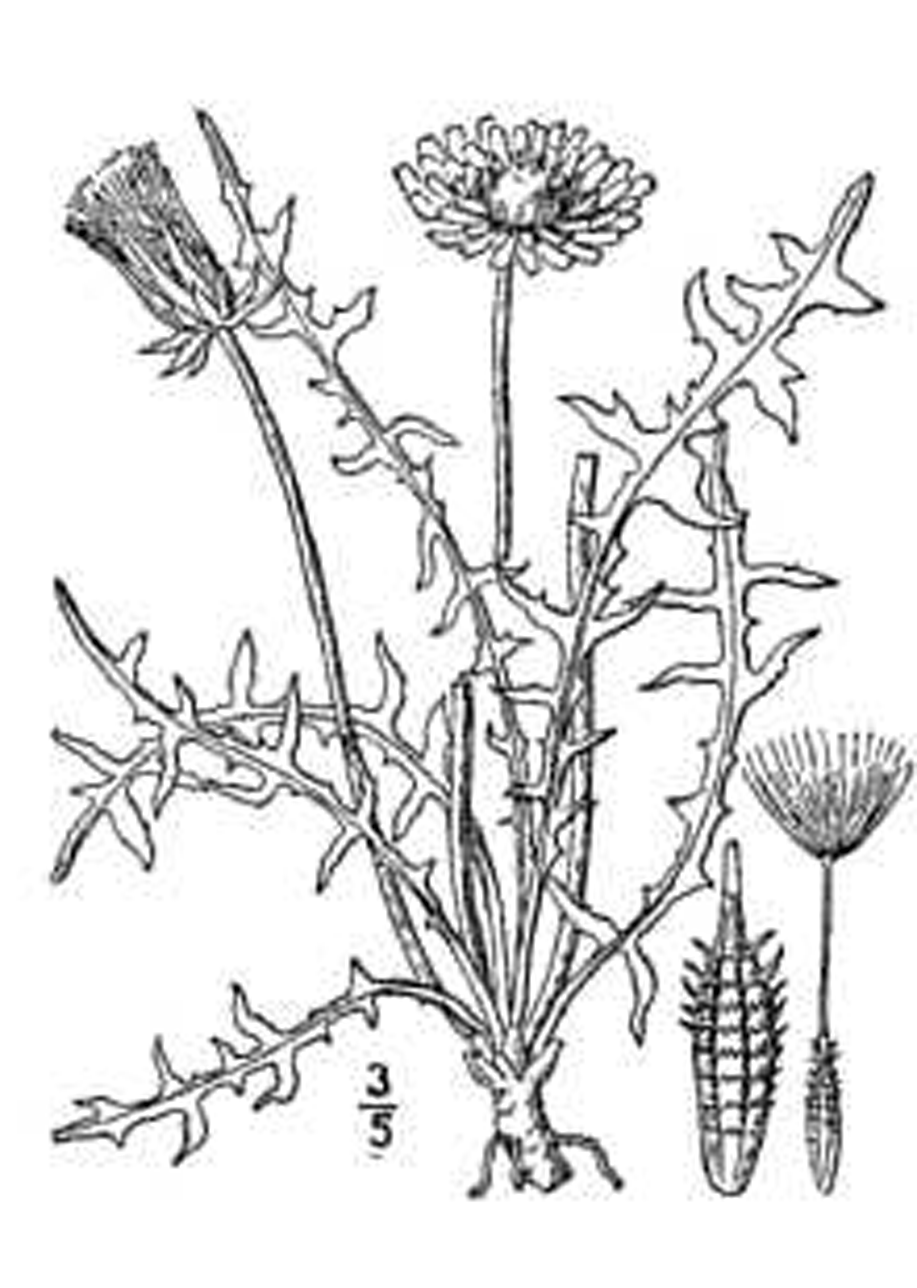
It is a perennial plant consisting of a rosette of leaves with flowering stalks. Simple basal leaves are 2 ½ to 10 inches long. Leaf has triangular lobes along its length, usually broader at the outer tip than at the base. There is a central vein along the entire length that is hallow and contains a milky juice. Leaves form a rosette on the ground, above the central tap root. The tap root can grow up to a length of 3 feet. This taproot is dark brown in color, contains milky juice and is somewhat fleshy. Rising from the center of the rosette is one or more flowering stalks, usually 12" but can reach a height of 18". Flower stalks, usually light green sometimes are found light reddish green towards the base, are hallow and contain a milky juice. A yellow to orange flowerhead develops at the end of the flower stalk, usually 1 to two inches in diameter. Flowers open during the day but close at night.Flowers can be found from early spring to late fall, with the most productive time being from late Spring to early summer. The flowerhead produces the fruit or "achenes" that is light brown, light gray, or slightly olive green. This achenes in turn developed into the familiar "parachute" ; the hair-like parachutes which are feather like in appearance are called pappus.
Food:
Dandelions can be used in any number of different ways. Both the leaves and roots are used fresh or dried in teas. Leaves can be used in salads or cooked as with any green, and the flowers are used to make wine.
• Leaves can be blanched in the same way as endive
• The young leaves may also be boiled as a vegetable, spinach fashion, thoroughly drained, sprinkled with pepper and salt
• Can be used as an ingredient in simple vegetable soup
• Young leaves can eaten raw in a salad
• Roasted roots used as a substitute for coffee
Dandelion Coffee :
Roots are cleaned and dried. Dried roots are then roasted until they are coffee colored. They are then ground and prepared as you would coffee. Taste is very similar to coffee.
Medical Uses:
Both the dandelions root and leaves have been one of the most beneficial herbal remedies for centuries.
• Used to treat liver diseases, kidney diseases, and spleen problems.
• Used to treat the gall bladder.
• Used as a mild laxative.
• Helpful in the treatment of rheumatism, arthritis, and gout.
• Helpful in the prevention of gallstones.
Harvesting:
Roots can be harvested year round. Leaves are best before reaching maturity, however mature leaves are also eaten. Roots can be used fresh or dried. Roots should be cut into 3 to 6 inch long pieces before drying. Depending on the weather roots will take up to two weeks to dry. Dried roots should be brittle and snap when broken with the inside being white and not gray. Dried roots should be stored in a dark cool area in a sealed container.